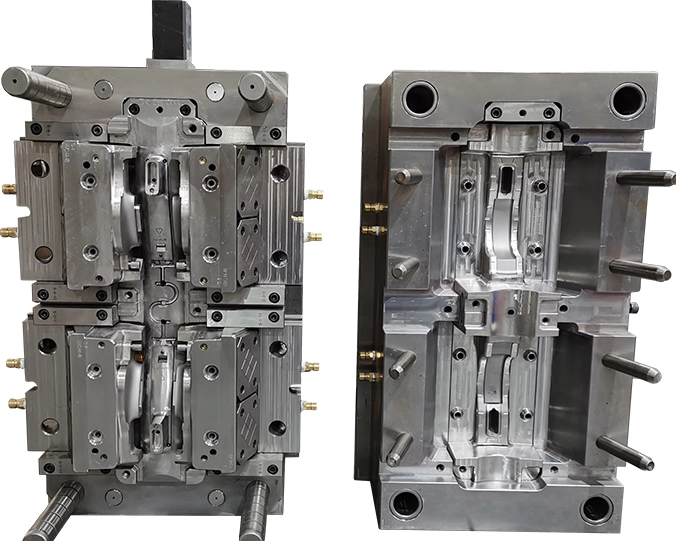
Gas & Water Assisted Injection Mold
Since the thermal conductivity and heat capacity of water are much bigger than nitrogen, so the injection cycle of water-assisted is about 70% shorter than the injection cycle of gas-assisted molding; The product wall thickness of water-assisted injection molding is more even than gas-assisted; The inner wall roughness of water-assisted injection molding is smoother than that gas-assisted injection molding.
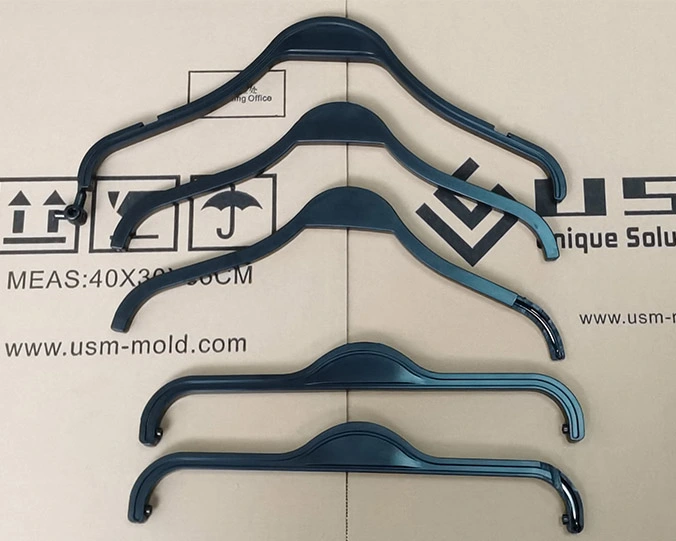
WATER & GAS ASSISTED INJECTION MOLDED PRODUCTS
Gas Assisted & Water Assisted Injection Molding Differences
1. Water-assisted injection molding uses water, and Water injection moulding can be recycled and reused, so the medium water of the two molding processes is cheaper than nitrogen;
2. Water-assisted injection molding equipment cost is nearly 10 times higher than gas-assisted injection molding, and Water assisted injection molding only can be imported currently;
3. Water-assisted injection molding can only be used for full injection but not short shot;
4. The plastic materials application in the gas-assisted injection molding process is more extensive than that of water-assisted injection molding;
5. The water-assisted injection moulding cost is much higher than that of gas injection mold.
Gas-Assisted Injection Molding Process
Gas-assisted injection molding is roughly divided into 4 stages: plastic injection, gas injection, pressure-holding cooling, and gas discharge.
1. Plastic injection: First, the plastic melt is injected into the mold cavity until the melt fills 75% to 95% of the cavity. The amount of pre-injection varies from product to product in actual production, and the melt encounters a lower temperature. The cavity wall forms a thinner solidified layer. This initial stage is roughly equivalent to the early stage of mold filling in the conventional injection molding process. Compared with the conventional molding process, because the cavity is only partially filled, and the air passage in the mold also facilitates the flow of the melt, the required molding pressure is low. In addition, this process is an under-material injection process. At this time, if too much material is used, it is easy to cause melt accumulation, and sink marks will occur where there is too much material; if there is too little material, it will cause blow-through.
2. Gas injection: Inject the gas (generally nitrogen) with a certain volume or pressure into the cavity. At this stage, it is necessary to accurately determine the switching time from the injection of the melt to the injection of nitrogen, and the correct determination of the gas pressure, these are related to the product quality, and many gas-assisted injection molded products defects may occur at this stage, the short-time delay switching is to control the thickness of the condensate layer, adjust the gas flow space, and cool the plastic at the gate to prevent gas backflow (gas backflow from the gating system instead of flowing according to the preset air passage).
3. Pressure-holding cooling: A certain gas pressure must be maintained after the cavity and core are filled, the gas is pressed from the inside to the outside to ensure that the outer surface of the product is close to the mold wall; and through the second penetration of the gas (the gas continues inside the plastic Penetration) to make up for the cooling shrinkage of the product from the inside, gas pressure holding generally includes two stages: high-pressure holding and low-pressure holding.
4. Air discharge: After the product has been cooled and shaped by holding pressure, the gas in the cavity and core can be discharged through the vent needle or the sprue, and then the mold can be opened to eject the product. It should be noted that the injection gas in this gas-assisted injection molding process must be discharged before the mold is opened, the product will swell or even break if the pressure gas is not discharged in time.
Gas-assisted Injection Molding Classification
1. Under-material injection molding: under-material injection molding is also called short shot, inject part of the plastic melt (usually 50%-90% of the cavity volume) into the mold cavity first, and then inject gas to use push the melt to complete mold filling and pressure holding by gas, the gas injection time and gas pressure are very important to the product quality, to inject the gas too early or pressure is too high will cause the gas to penetrate the melt front, otherwise it will lead to incomplete feeding and surface defects. In this type of gas injection moulding process, when the gas pressure is too high and the gas is injected too early, gas penetration cannot be avoided, if the gas pressure is too low and the gas is injected too late, the gas will not enter the plastic and will not be able to promote the flow of the melt front. Increasing the initial air pressure can avoid stagnation of the forward melt, and there will be no traces on the surface of the product, the under-material injection process is suitable for the molding of rod-shaped products or plate-shaped products with partial walls thickness.
2. Full material injection: in the full material injection process, the mold cavity and core are completely filled with melt plastic, and then gas is injected, since the mold cavity and core have been filled, the gas can only enter when the melt volume shrinks. Therefore, the gas-only plays a role in maintaining pressure. the pressure holding effect is more effective, the main advantage of full gas assisted injection molded products which will not have sink marks or warpage, and meets the requirements of high-quality products.
3. Overflow cavity molding: a secondary cavity and core (overflow cavity and core) connected to the main cavity is designed outside the mold cavity and core, and a control valve is set between the cavity with core and the overflow cavity with core, when the injection is started, the secondary cavity and core are closed, the melt fills the main cavity and core, and then the second cavity with the core is opened to start gas injection, the injected gas forces a part of the melt into the sub-cavity with core, and at this time the sub-cavity with the core is closed again to enter the gas pressure holding stage, by adopting this method, it is easy to control the injection volume of the melt, there is no switching mark on the product surface, and the welding mark is eliminated, this process is conducive to the formation of perfect surface and uniform wall thickness for rod-shaped products, and is used to solve the sink mark and warpage defects of the product.
4. Melt reflow molding: this process is similar to the overflow cavity with the core molding method, the plastic is injected from one side of the mold, and the gas is injected at the other end of the mold, first, the plastic completely fills the mold, and after a preset period of time, gas is injected through the gas injection element, after the gas is injected, the plastic is pushed back into the barrel of the injection molding machine again.

 English
English русский
русский