Design standard of exhaust slot
The exhaust system should ensure that the gas in the cavity is smoothly discharged, and also prevent the material from entering and exhausting channels from causing flashing of the product or blockage of the gas channel during mass production, most plastic mold factories and plastic mold suppliers only know that they need to open an exhaust slot, but they don’t how large is reasonable. So the cross-sectional size design at the entrance of the exhaust system is very important, in order to meet the above requirements, the inlet section of the exhaust system is usually designed as a gap with a larger aspect ratio (h/w) (see pictue 1), and the gap depth (exhaust gap or exhaust slot depth) h, which is less than the overflow value of the material into the mold is limited, generally 0.02-0.05mm; the gap width w is determined according to the gap depth H and the cross-sectional area A of the exhaust passage required to discharge the gas in the mold cavity during the filling time (w≥A /h).

The cross-sectional area A of the exhaust channel is calculated as follows: A=0.05V/N
In the formula: A exhaust channel cross-sectional area mm²
V—total volume of cavity and pouring system, cm³
n——the number of exhaust slots

The overflow value is the smallest gap that the material can flow into, the overflow value of the molding material depends on the fluidity of the material determined by the material characteristics and process conditions. The better the fluidity, the smaller the overflow value, tThe overflow values of commonly used plastics and conventional molding conditions are shown in picture 2 in the following table.
Picure 3 shows the design standard of the exhaust slot, and picture 4 shows the wrong opening method of the exhaust slot.

Plastic part ribs desigining
Jan 4, 2022The ribs function: The role of ribs is to improve the strength and rigidity of the plastic parts, prevent the plastic parts from being distorted and deformed, and will not cause the appearance of the...view
Conformal cooing channel of plastic injection mold
Feb 23, 2022The conformal cooling gate is a new type of mold cooling gate based on 3D printing technolog, because of its processing characteristics, the conformal cooling gate can fit the shape of the product...view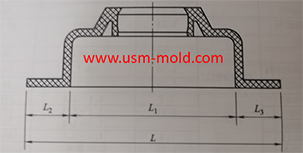
Plastic molding shrinkage rate
Dec 30, 2021Plastic parts getting smaller by shrink, due to the temperature decrease during the molding process, and the shrinkage is expressed by the shrinkage rate, it is common plastic shrinkage rates are...view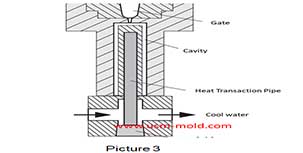
Plastic injection mold common cooling gate
Feb 17, 20221. Straight-through cooling water gate: the straight-through cooling gate is the most commonly used gate for plastic injection mold, and it is also the most convenient type of cooling for processing....view
Plastic injection mold runner system design points
Jan 9, 2022When designing the gating system, Firstly, we should consider making the plastic melt fill the cavity with core side quickly to reduce pressure and heat loss; secondly, it should be economically...view
Water assisted injection molding introduction
May 11, 2022Like the gas-assisted injection molding process, water-assisted injection molding injects a piece of plastic into the mold cavity and core firstly, and then injects water to squeeze the melt plastic...view
 English
English русский
русский